- How To Numpy For Python 3.6 Macros
- Numpy Package In Python
- How To Numpy For Python 3.6 Mac Os
- Python Numpy Pdf
- How To Numpy For Python 3.6 Macro
- Numpy Download
Posted on October 4, 2016 by Paul
Updated 26 January 2020
In this article, I will show you how to install Python 3 with NumPy, SciPy and Matplotlib on macOS Catalina.
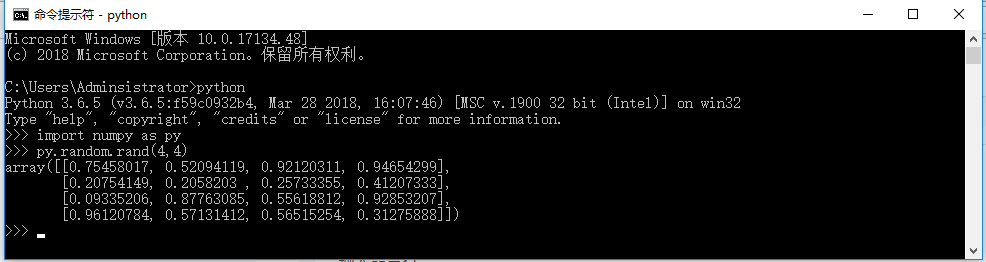
Installing GDAL (Python 3.6) on Mac OS X. GitHub Gist: instantly share code, notes, and snippets. Gdalmerge.py seems to need numpy, and this is not part of. NumPy adds a fast and sophisticated array facility to the Python language and is the fundamental package needed for scientific computing with Python. The NumPy package contains: a powerful N-dimensional array object sophisticated (broadcasting) functions basic linear algebra functions basic Fourier transforms sophisticated random. I had installed Python 3.6 in my windows laptop from python.org. After that I ran cmd and did pip install numpy and pip install numpy. It installed successfully. Homebrew is a package manager for Mac OS X. Here's how to install it beforehand. Next, let's upgrade our default installation of Python to something greater than 2.7. Step 1 - Install Libraries Pip. Pip is a package manager for Python. Easyinstall pip.
Millions of developers and companies build, ship, and maintain their software on GitHub — the largest and most advanced development platform in the world.
There is also a video version of this tutorial:
MacOS comes by default with Python 2.7 which, at this point, receives only bug fixes and will be EOL by 2020. Python 3.x is the future and it is supported by all major Python libraries. In this tutorial, we’ll use Python 3.8.
Start by installing the Command Line Tools for macOS. Please note, that you will need the Command Line Tools even if you’ve already installed Xcode. Open a Terminal and write:
Once the Command Line Tools are installed, we can install Python.
The official installer of Python is a pkg file that will start a GUI installer which will guide you through the installation. You can also check the video version of this tutorial if you want to see how I did it.
As a side note, you can have multiple Python 3 versions installed on your macOS machine. If this is the case, you can select which version you want to use by specifying the version number, e.g.:
How To Numpy For Python 3.6 Macros
or:
After the above, you can invoke Python 3.8 using the python3.8 command. python3 will also invoke the latest installer version of Python 3. This is what I see if I run python3.8 on my machine:
Next, let’s follow best practices and create a new Python environment in which we can install NumPy, SciPy and Matplotlib:
At this point, your prompt should indicate that you are using the work environment. You can read more about Python environment in the documentation.
Once an environment is activated, all the install commands will apply only to the current environment. By default, if you close your Terminal, the environment is deactivated. If you want to be able to use it, use the source work/bin/activate command.
We can install NumPy, SciPy and Matplotlib with:
As a side note, when you are in an active environment you can use the python command to invoke the Python interpreter, no need to use the version number.
Fire up Python, import scipy and print the version of the installed library. This is what I see on my machine:
Let’s try something a bit more interesting now, let’s plot a simple function with Matplotlib. First, we’ll import SciPy and Matplotlib with:
Next, we can define some points on the (0, 1) interval with:
Now, let’s plot a parabola defined on the above interval:
Numpy Package In Python
You should see something like this:
As you’ve probably noticed, plt.show() is a blocking command. You won’t be able to use the interpreter until you close Figure 1.
There is also an interactive mode in which you can plot functions. Close Figure 1 and write:
How To Numpy For Python 3.6 Mac Os
This is what you should see:
Python Numpy Pdf
At any point you can disable the interactive plot mode with:
after which you will need to use the plt.show() function in order to actually see the result of the plt.plot function.
How To Numpy For Python 3.6 Macro
If you want to learn more about Python and Matplotlib, I recommend reading Python Crash Course by Eric Matthes. The book is intended for beginners, but has a nice Data Visualization intro to Matplotlib chapter:
Another good Python book, for more advanced users, which also uses Matplotlib for some of the book projects is Python Playground by Mahesh Venkitachalam: